Regularizers Description¶
This page describes the features and cases of usage of the regularizers, that have already been implemented in the core of BigARTM library. Detailed description of parameters of the regularizers in the Python API can be seen in Regularizers.
Examples of the usage of the regularizers can be found in Python Tutorial and in Python Guide.
Note: The influence of any regularizer with tau parameter in it’s M-step formula can be controlled via this parameter.
Smooth/Sparse Phi¶
- M-step formula:
p_wt 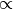 (
(n_wt + tau * f(p_wt) * dict[w])
- Description:
This regularizer provides an opportunity to smooth or to sparse subsets of topics using any specified distribution.
To control the type of the distribution over tokens one can use the dictionary (dict), and the function f. dict is an object of Dictionary class, containing list with all unique tokens and corresponding list of values, which can be specified by the user. These values are dict[w]. f is a transform function, the derivative of the function under the KL-divergence in the source formula of the regularizer.
If the dictionary is not specified, all values will be 1. If is specified, and there’s no value for the token in it, the token will be skipped. The f is const 1 by default.
- Usage:
There’re several strategies of usages of this regularizer:
- simply smooth or sparse all values in the
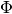 matrix with value
matrix with value n: create one regularizer and assigntauton; - divide all topics into two groups (subject and background), sparse first group to increase their quality and smooth second one to gather there all background tokens: create two regularizers, specify
topic_namesparameters with corresponding list in both ones and settauin sparsing regularizer to some negative value, and in smoothing to some positive one; - smooth or sparse only tokens of specified modalities: create one regularizer and specify parameter
class_idswith list of names of modalities to be regularized; - smooth or sparse only tokens from pre-defined list: edit the Dictionary object of the collection and change
valuefield of the dictionary for tokens from this list should be set to some positive constant (remember, that it will bedict[w]in formula), and for other tokensvaluefield should be set to 0; - increase the influence on the small
p_wtvalues and reduce on the big: define theffunction by specifying theKlFunctionInfoobject tokl_function_infoparameter (don’t forget, thatfwill be the derivative of this function).
All these strategies can be transformed, merged to each other etc.
- Notes:
- smoothing in second strategy should be started from the start of model learning and be constant;
- sparsing should start after some iterations and it’s influence should increase gradually;
- setting different values to
valuefield for tokens from pre-defined list in pre-last strategy gives an opportunity to deal with each token as it is necessary.
Smooth/Sparse Theta¶
- M-step formula:
p_td 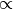 (
(n_td + tau * alpha_iter[iter] * f(p_td) * mult[d][t])
- Description:
This regularizer provides an opportunity to smooth or to sparse subsets of topics in 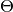 matrix.
matrix.
To control the influence of the regularizer on each document pass one can use alpha_iter parameter, which is a list with length equal to number of passes through the document, and the function f. f is a transform function, the derivative of the function under the KL-divergence in the source formula of the regularizer.
If alpha_iter is not specified, it is 1 for all passes. The f is const 1 by default.
Also you can control the regularization of any document for any topic, or set a general mask for all documents, that specifies mult coef for each topic.
- Usage:
There’re several strategies of usages of this regularizer:
- simply smooth or sparse all values in the
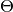 matrix with value
matrix with value n: create one regularizer and assigntauton; - divide all topics into two groups (subject and background), sparse first group to increase their quality and smooth second one to gather there all background tokens: create two regularizers, specify
topic_namesparameters with corresponding list in both ones and settauin sparsing regularizer to some negative value, and in smoothing to some positive one; - increase the influence of the regularizer on later passes through the document: specify
alpha_iterlist withkvalues from smaller to greater, wherekis a number of passes though the document; - increase the influence on the small
p_tdvalues and reduce on the big: define theffunction by specifying theKlFunctionInfoobject tokl_function_infoparameter (don’t forget, thatfwill be the derivative of this function). - influence only specified documents in specified way using
multvariable. This can be used as the custom initialization of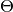 matrix.
matrix.
All these strategies can be transformed, merged to each other etc.
- Notes:
- smoothing in second strategy should be started from the start of model learning and be constant;
- sparsing should start after some iterations and it’s influence should increase gradually;
- fitting (with regularization or not) will be different in cases of
ARTM.reuse_thetaflag set to True or False.
Decorrelator Phi¶
- M-step formula:
p_wt 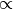 (
(n_wt - tau * p_wt * 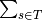 (
(p_ws))
- Description:
This regularizer provides an opportunity to decorrelate columns in the 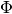 matrix (e.g. make topics more different), that allows to increase the interpretability of topics.
matrix (e.g. make topics more different), that allows to increase the interpretability of topics.
- Usage:
There’re several strategies of usages of this regularizer:
- decorrelate all topics: one regularizer with
tau, that should be tuned experimentally; - in the strategy with two background and subject topics it is recommended to deal with each group separately: create two decorrelators and specify
topic_namesparameter in them, as it was done for Smooth/sparse regularizers; - deal only with the tokens of given modality: set
class_idsparameter the list with names of modalities to use in this regularizer.
All these strategies can be transformed, merged to each other etc.
- Notes:
- this is a sparsing regularizer, it works well with general sparsing
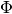 regularizer;
regularizer; - the recommendation is to run this regularizer from the beginning of the fitting process.
- this is a sparsing regularizer, it works well with general sparsing
Label Regularization Phi¶
- M-step formula:
p_wt 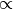
n_wt + tau * dict[w] * (p_wt * n_t) / (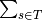 (
(p_ws * n_s))
Specified sparse Phi¶
- Description:
It is not a usual regularizer, it’s a tool to sparse as many elements in 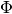 , as you need. You can sparse by columns or by rows.
, as you need. You can sparse by columns or by rows.
Topic Selection Theta¶
- M-step formula:
p_td 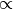
n_td - tau * n_td * topic_value[t] * alpha_iter[iter],
where topic_value[t] = n / (n_t * |T|)
Hierarchy Sparsing Theta¶
ToDo(nadiinchi)
Topic Segmentation Ptdw¶
ToDo(anastasiabayandina)
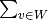
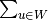 (
( where
where 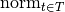 (
(