BigARTM v0.7.0 Release notes¶
We are happy to introduce BigARTM v0.7.0, which brings you the following changes:
- New-style models
- Network modus operandi is removed
- Coherence regularizer and scores (experimental)
New-style models¶
BigARTM v0.7.0 exposes new APIs to give you additional control over topic model inference:
- ProcessBatches
- MergeModel
- RegularizeModel
- NormalizeModel
Besides being more flexible, new APIs bring many additional benefits:
- Fully deterministic inference, no dependency on threads scheduling or random numbers generation
- Less bottlenecks for performance (DataLoader and Merger threads are removed)
- Phi-matrix regularizers can be implemented externally
- Capability to output Phi matrices directly into your NumPy matrices (scheduled for BigARTM v0.7.2)
- Capability for store Phi matrices in sparse format (scheduled for BigARTM v0.7.3)
- Capability for async ProcessBatches and non-blocking online algorithm (BigARTM v0.7.4)
- Form solid foundation for high performance networking (BigARTM v0.8.X)
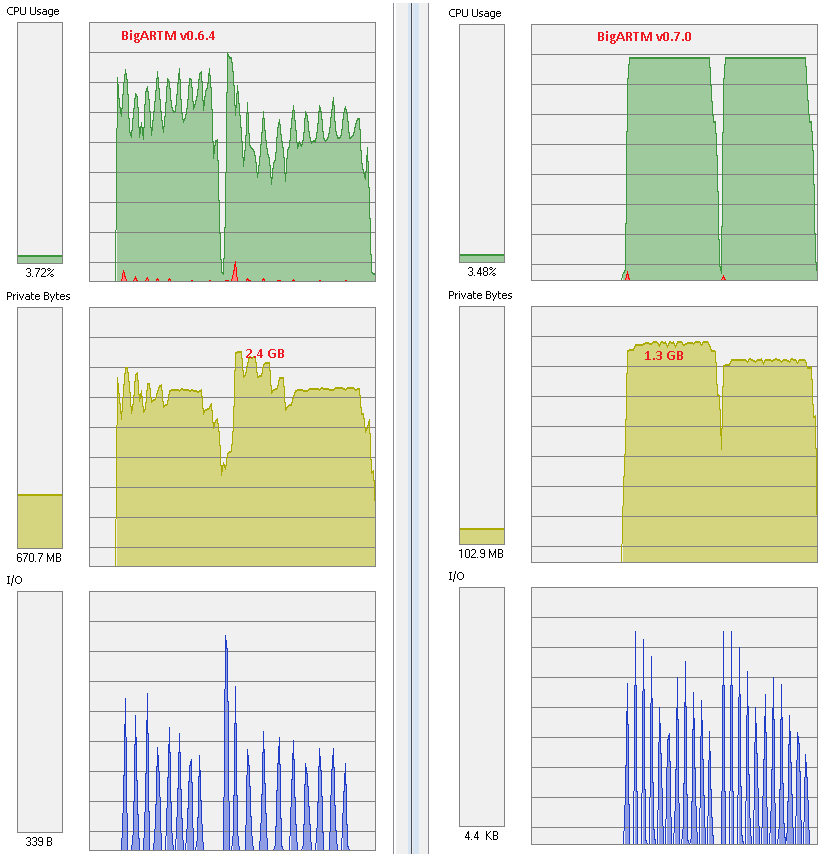
The picture below illustrates scalability of BigARTM v0.7.0 vs v0.6.4. Top chart (in green) corresponds to CPU usage at 28 cores on machine with 32 virtual cores (16 physical cores + hyper threading). As you see, new version is much more stable. In addition, new version consumes less memory.
Refer to the following examples that demonstrate usage of new APIs for offline, online and regularized topic modelling:
Models, tuned with the new API are referred to as new-style models, as opposite to old-style models inferred with AddBatch, InvokeIteration, WaitIdle and SynchronizeModel APIs.
Warning
For BigARTM v0.7.X we will continue to support old-style models. However, you should consider upgrading to new-style models because old APIs (AddBatch, InvokeIteration, WaitIdle and SynchronizeModel) are likely to be removed in future releases.
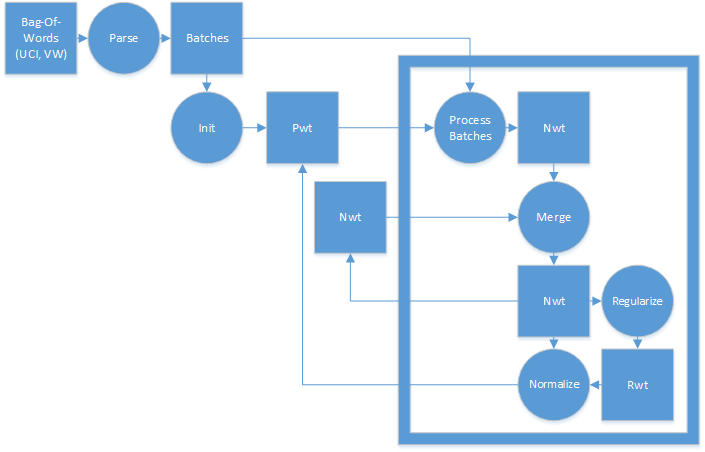
The following flow chart gives a typical use-case on new APIs in online regularized algorithm:
Notes on upgrading existing code to new-style models
New APIs can only read batches from disk. If your current script passes batches via memory (in AddBatchArgs.batch field) then you need to store batches on disk first, and then process them with ProcessBatches method.
Initialize your model as follows:
- For python_interface: using MasterComponent.InitializeModel method
- For cpp_interface: using MasterComponent.InitializeModel method
- For c_interface: using ArtmInitializeModel method
Remember that you should not create ModelConfig in order to use this methods. Pass your topics_count (or topic_name list) as arguments to InitializeModel method.
Learn the difference between Phi and Theta scores, as well as between Phi and Theta regularizes. The following table gives an overview:
Object Theta Phi Scores - Perplexity
- SparsityTheta
- ThetaSnippet
- ItemsProcessed
- SparsityPhi
- TopTokens
- TopicKernel
Regularizers - SmoothSparseTheta
- DecorrelatorPhi
- ImproveCoherencePhi
- LabelRegularizationPhi
- SmoothSparsePhi
- SpecifiedSparsePhi
Phi regularizers needs to be calculated explicitly in RegularizeModel, and then applied in NormalizeModel (via optional rwt argument). Theta regularizers needs to be enabled in ProcessBatchesArgs. Then they will be automatically calculated and applied during ProcessBatches.
Phi scores can be calculated at any moment based on the new-style model (same as for old-style models). Theta scores can be retrieved in two equivalend ways:
pwt_model = "pwt" master.ProcessBatches(pwt_model, batches, "nwt") perplexity_score.GetValue(pwt_model).value
or
pwt_model = "pwt" process_batches_result = master.ProcessBatches(pwt_model, batches, "nwt") perplexity_score.GetValue(scores = process_batches_result).value
Second way is more explicit. However, the first way allows you to combine aggregate scores accross multiple ProcessBatches calls:
pwt_model = "pwt" master.ProcessBatches(pwt_model, batches1, "nwt") master.ProcessBatches(pwt_model, batches2, "nwt", reset_scores=False) perplexity_score.GetValue(pwt_model).value
This works because BigARTM caches the result of ProcessBatches together (in association with pwt_model). The reset_scores switch disables the default behaviour, which is to reset the cache for pwt_model at the beginning of each ProcessBatch call.
Continue using GetThetaMatrix and GetTopicModel to retrieve results from the library. For GetThetaMatrix to work you still need to enable cache_theta in master component. Remember to use the same model in GetThetaMatrix as you used as the input to ProcessBatches. You may also omit “target_nwt” argument in ProcessBatches if you are not interested in getting this output.
master.ProcessBatches("pwt", batches) theta_matrix = master.GetThetaMatrix("pwt")
Stop using certain APIs:
- For python_interface: stop using class Model and ModelConfig message
- For cpp_interface: stop using class Model and ModelConfig message
- For c_interface: stop using methods ArtmCreateModel, ArtmReconfigureModel, ArtmInvokeIteration, ArtmAddBatch, ArtmWaitIdle, ArtmSynchronizeModel
Notes on models handling (reusing, sharing input and output, etc)
Is allowed to output the result of ProcessBatches, NormalizeModel, RegularizeModel and MergeModel into an existing model. In this case the existing model will be fully overwritten by the result of the operation. For all operations except ProcessBatches it is also allowed to use the same model in inputs and as an output. For example, typical usage of MergeModel involves combining “nwt” and “nwt_hat” back into “nwt”. This scenario is fully supported. The output and input of ProcessBatches must refer to two different models. Finally, note that MergeModel will ignore all non-existing models in the input (and log a warning). However, if none of the input models exist then MergeModel will thrown an error.
Known differences
Decorrelator regularizer will give slightly different result in the following scenario:
master.ProcessBatches("pwt", batches, "nwt") master.RegularizeModel("pwt", "nwt", "rwt", phi_regularizers) master.NormalizeModel("nwt", "pwt", "rwt")
To get the same result as from model.Synchronize() adjust your script as follows:
master.ProcessBatches("pwt", batches, "nwt") master.NormalizeModel("nwt", "pwt_temp") master.RegularizeModel("pwt_temp", "nwt", "rwt", phi_regularizers) master.NormalizeModel("nwt", "pwt", "rwt")
You may use GetThetaMatrix(pwt) to retrieve Theta-matrix, previously calculated for new-style models inside ProcessBatches. However, you can not use GetThetaMatrix(pwt, batch) for new models. They do not have corresponding ModelConfig, and as a result you need to go through ProcessBatches to pass all parameters.
Network modus operandi is removed¶
Network modus operandi had been removed from BigARTM v0.7.0.
This decision had been taken because current implementation struggle from many issues, particularly from poor performance and stability. We expect to re-implement this functionality on top of new-style models.
Please, let us know if this caused issues for you, and we will consider to re-introduce networking in v0.8.0.
Coherence regularizer and scores (experimental)¶
Refer to example in example16_coherence_score.py.